A Bold Convention
A proposed treaty drafted by the International Coalition for Animal Protection (ICFAP) and informed by the One Health concept, the Convention on Animal Protection for Public Health, Animal Well-Being, and the Environment (CAP) holds the promise of becoming the first umbrella treaty to advance the interests of animals on the international stage.
Championed by a diverse array of stakeholders, CAP creates a much-needed space in which States and stakeholders can address critical issues concerning our interactions with and need to protect animals on an ongoing and evolving basis.
The current version of the CAP represents two years of drafting with significant input from a broad range of experts in animal law, environmental law, public health, and international trade and policy. CAP’s umbrella framework establishes minimum standards that govern our interactions with and treatment of animals. Issue-focused protocols, which could be agreed under the framework treaty, will allow States to negotiate specific additional standards. By providing for biennial Conferences of the Parties, the treaty will empower States to consistently engage on these issues and to adapt to changing societal norms or conditions, scientific discoveries, and more.
So concretely what does the CAP seek to do?
CAP's Principles
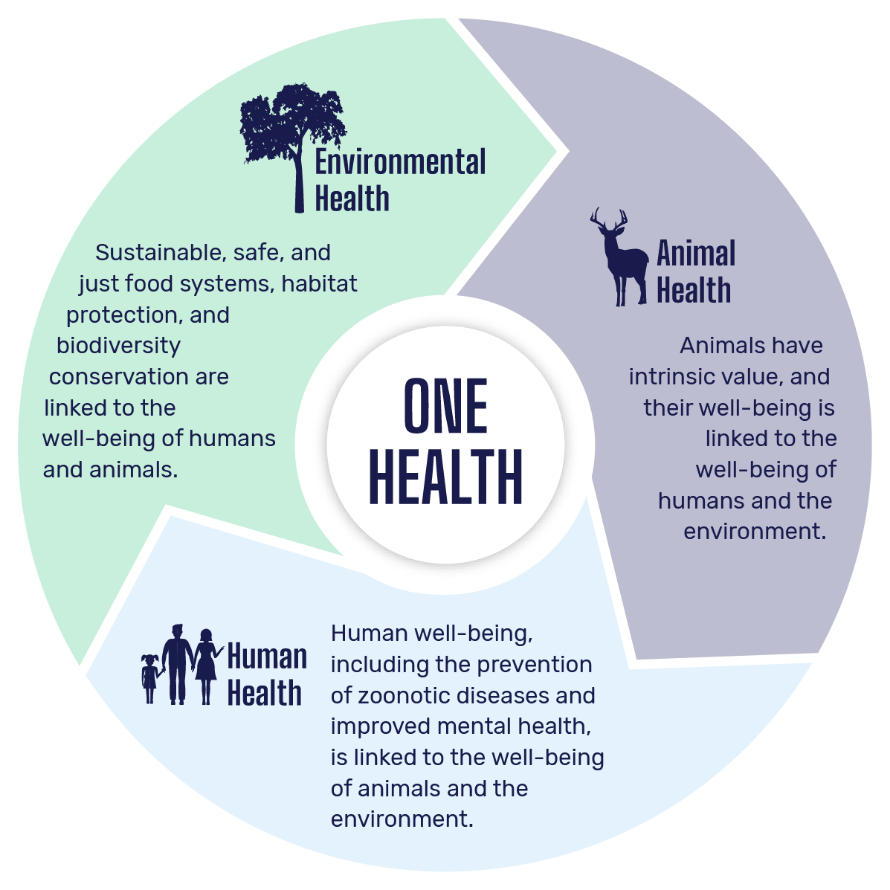
- Humans and animals share an evolutionary heritage and co-exist within interdependent ecosystems. Animals’ individual and collective well-being and the health of their supporting ecosystems are integral to public health, environmental protection, and conservation.
- As sentient beings, animals have intrinsic value. Humans have an ethical obligation to act responsibly toward animals. No animal should be subjected to cruel acts or unnecessary suffering.
- When animals are under human control, a positive obligation exists to ensure their well-being by providing them with an adequate, species-specific environment and care appropriate for their particular needs.
- Subjecting animals to physical, psychological, or environmental stressors is detrimental to their well-being and increases their susceptibility to contracting and transmitting disease.
- Protecting global public health requires States to take a precautionary approach in regulating human interaction with animals to prevent the emergence and spread of pathogens.
CAP's main objectives
Provide a comprehensive, non-regressive, legal framework on animal welfare as part of the ONE HEALTH approach.
Animal welfare
- Urge States to take comprehensive measures to ensure the well-being of animals, including animals under human control and wild animals. Prevention of cruelty or unnecessary pain towards animals.
- Prevention of cruelty or unnecessary pain towards animals.
Animals and the environment
- Promote the conservation of animals within their natural habitat.
- Urge stakeholders to understand the importance of animal protection in the preservation of our environment.
Animals and public health
- Minimize spread of pathogens.
- Regulate high-risk practices.
- Prevent antimicrobial resistance.



